Cousin explanation chart
Author: u | 2025-04-23
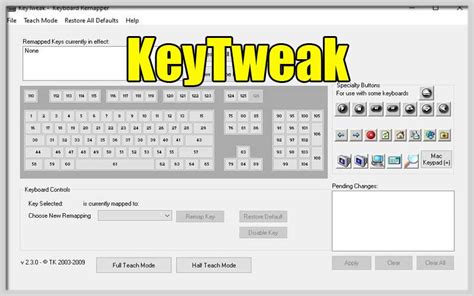
Chart Of Cousin Relationships. Cousin relationships genealogy branches template ancestry understanding Cousin relation explanation Family cousin cousins chart relationships Nice Cousins chart with explanation.

My Explanation of the Cousins Chart
Wife (Emma) is David's first cousin.AdamAgathaBettyBenCharlesCorindaDavidEmmaEricMaternal or paternal cousinA term that specifies whether one individual is a cousin of another through the mother's side of the family (maternal) or the father's side (paternal). If the relationship is not equally paternal for both or equally maternal for both, then the paternal cousin of one is the maternal cousin of the other.Emma and David are paternal first cousins (being related through their fathers). Emma is also Natalia's paternal first cousin (as related on Natalia's father's side), but Natalia is Emma's maternal first cousin (as related on Emma's mother's side). David and Natalia would only be related if they shared a common ancestor.AdamAgathaLukeLauraBettyBenCharlesCorindaMarkMaudDavidEmmaNataliaRelationship chartsCousin chartA "cousin chart", or "table of consanguinity", is helpful in identifying the degree of cousin relationship between two people using their most recent common ancestor as the reference point. Cousinship between two people can be specifically described in degrees and removals by determining how close, generationally, the common ancestor is to each person.[2]If one person's →ParentGrandparentGreat-grandparentGreat-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-great-grandparentIs the other person's↓Then they are ↘ParentSiblingsParent/Child or Uncle/AuntGrandparent/GrandchildGreat grandparent/Great grandchildGreat great grandparent/Great great grandchildGreat great great grandparent/Great great great grandchildGrandparentParent/Child or Uncle/Aunt1st cousins1st cousins once removed1st cousins twice removed1st cousins3× removed1st cousins 4× removedGreat-grandparentGreat-uncle/Great-aunt1st cousins once removed2nd cousins2nd cousins once removed2nd cousins twice removed2nd cousins3× removedGreat-great-grandparentGreat-great-uncle/Great-great-aunt1st cousins twice removed2nd cousins once removed3rd cousins3rd cousins once removed3rd cousins twice removedGreat-great-great-grandparent Great-great-great-uncle/Great-great-great-aunt1st cousins 3× removed2nd cousins twice removed3rd cousins once removed4th cousins4th cousins once removedGreat-great-great-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-great-uncle/Great-great-great-great-aunt1st cousins 4× removed2nd cousins 3× removed3rd cousins twice removed4th cousins once removed5th cousinsCanon law relationship chart Canon Law Relationship Chart. See an example of how to use chart. Another visual chart used in determining the legal relationship between two people who share a common ancestor is based upon a rhombus shape, usually referred to as a "canon law relationship chart".The chart is used by placing the "common progenitor" (the most recent person from whom both people (A and B) are descended) in the top space in the diamond-shaped chart, and assigning a direction (arbitrarily, left or right) to each of the two people, A and B. Then follow the line down the outside edge of the chart for each of the two people until their respective relationship to the common ancestor is reached. Upon determining that place along the opposing outside edge for each person, their relationship is then determined by following the lines inward to the point of intersection. The information contained in the common "intersection" defines the relationship.For a simple example, in the illustration to the right, if two siblings use the chart to determine their relationship, their common parent (either one, if there are two) is placed in the topmost position, and each child is assigned the space below and along the outside of the chart. Then, following the spaces inward, they would intersect in the "brother" diamond.[3] If their children want to determine their relationship, they would follow the path established by their parents but descend an additional step below along the outside of the chart Chart Of Cousin Relationships. Cousin relationships genealogy branches template ancestry understanding Cousin relation explanation Family cousin cousins chart relationships Relationship terminology can be confusing, but we've compiled a guide to explain how you are related to that cousin three times removed.That’s a question that we have been asked quite a bit lately, and sometimes determining that exact familial connection with someone else can be confusing.What is the difference between a second cousin and a first cousin, once removed?What does the “removed” mean, anyway?If my mom has a cousin, how is he related to me?Is my grandfather’s sister my great-aunt, or my grand-aunt?If you have ever felt confusion over these terms, you are not alone!Most of us know that our parents’ siblings’ children are our first cousins, and that our parents’ siblings themselves are our aunts and uncles. That’s easy enough to understand. It’s when you get to more distant connections that it becomes confusing.If you share the same grandparents, there is no difference in the generations, so you are first cousins. If you share the same great-grandparents, you are second cousins. If you share the same great-great-grandparents you are third cousins, and so on.However, if your grandparents are someone else’s great-grandparents, then you are first cousins once removed, because there is a generational gap between you. The thing to remember is that the “removed” is used when you and your relative are of different generations. For instance, you and your cousin’s child, or you and your father’s cousin are of different generations, so there is going to be a “removed” in a description of your relationship.The numerical value, “once removed” or “three times removed,” counts back how many generations you have to go to find the common ancestor between you and that other relative.For example, if your first cousin has children, those children are your first cousins once removed, because your grandparents are their great-grandparents (just one generation). If those children then have children, they are your first cousins twice removed, because your grandparents are their great-great-grandparents (which is two generations).Similarly, your mom’s cousin is your first cousin once removed, because his grandparents are your great-grandparents. There is a generational difference. However, your mom’s cousin’s CHILD is your second cousin with no “removed” added, because the two of you share the same great-grandparents. There is no generational difference between the two of you, so there is no “remove.”With regards to the difference between great-aunt, grand-aunt, etc. – this one is up to you! They're just different terms that mean the same thing. The siblings of your grandparents can be called either your great-aunts and great-uncles, or your grand-aunts and grand-uncles.The following chart may be helpful:The following DNA & Relationship Quick Reference Chart also helps identify the % of shared DNA between you and other relatives. Get your free pdfComments
Wife (Emma) is David's first cousin.AdamAgathaBettyBenCharlesCorindaDavidEmmaEricMaternal or paternal cousinA term that specifies whether one individual is a cousin of another through the mother's side of the family (maternal) or the father's side (paternal). If the relationship is not equally paternal for both or equally maternal for both, then the paternal cousin of one is the maternal cousin of the other.Emma and David are paternal first cousins (being related through their fathers). Emma is also Natalia's paternal first cousin (as related on Natalia's father's side), but Natalia is Emma's maternal first cousin (as related on Emma's mother's side). David and Natalia would only be related if they shared a common ancestor.AdamAgathaLukeLauraBettyBenCharlesCorindaMarkMaudDavidEmmaNataliaRelationship chartsCousin chartA "cousin chart", or "table of consanguinity", is helpful in identifying the degree of cousin relationship between two people using their most recent common ancestor as the reference point. Cousinship between two people can be specifically described in degrees and removals by determining how close, generationally, the common ancestor is to each person.[2]If one person's →ParentGrandparentGreat-grandparentGreat-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-great-grandparentIs the other person's↓Then they are ↘ParentSiblingsParent/Child or Uncle/AuntGrandparent/GrandchildGreat grandparent/Great grandchildGreat great grandparent/Great great grandchildGreat great great grandparent/Great great great grandchildGrandparentParent/Child or Uncle/Aunt1st cousins1st cousins once removed1st cousins twice removed1st cousins3× removed1st cousins 4× removedGreat-grandparentGreat-uncle/Great-aunt1st cousins once removed2nd cousins2nd cousins once removed2nd cousins twice removed2nd cousins3× removedGreat-great-grandparentGreat-great-uncle/Great-great-aunt1st cousins twice removed2nd cousins once removed3rd cousins3rd cousins once removed3rd cousins twice removedGreat-great-great-grandparent Great-great-great-uncle/Great-great-great-aunt1st cousins 3× removed2nd cousins twice removed3rd cousins once removed4th cousins4th cousins once removedGreat-great-great-great-grandparentGreat-great-great-great-uncle/Great-great-great-great-aunt1st cousins 4× removed2nd cousins 3× removed3rd cousins twice removed4th cousins once removed5th cousinsCanon law relationship chart Canon Law Relationship Chart. See an example of how to use chart. Another visual chart used in determining the legal relationship between two people who share a common ancestor is based upon a rhombus shape, usually referred to as a "canon law relationship chart".The chart is used by placing the "common progenitor" (the most recent person from whom both people (A and B) are descended) in the top space in the diamond-shaped chart, and assigning a direction (arbitrarily, left or right) to each of the two people, A and B. Then follow the line down the outside edge of the chart for each of the two people until their respective relationship to the common ancestor is reached. Upon determining that place along the opposing outside edge for each person, their relationship is then determined by following the lines inward to the point of intersection. The information contained in the common "intersection" defines the relationship.For a simple example, in the illustration to the right, if two siblings use the chart to determine their relationship, their common parent (either one, if there are two) is placed in the topmost position, and each child is assigned the space below and along the outside of the chart. Then, following the spaces inward, they would intersect in the "brother" diamond.[3] If their children want to determine their relationship, they would follow the path established by their parents but descend an additional step below along the outside of the chart
2025-03-26Relationship terminology can be confusing, but we've compiled a guide to explain how you are related to that cousin three times removed.That’s a question that we have been asked quite a bit lately, and sometimes determining that exact familial connection with someone else can be confusing.What is the difference between a second cousin and a first cousin, once removed?What does the “removed” mean, anyway?If my mom has a cousin, how is he related to me?Is my grandfather’s sister my great-aunt, or my grand-aunt?If you have ever felt confusion over these terms, you are not alone!Most of us know that our parents’ siblings’ children are our first cousins, and that our parents’ siblings themselves are our aunts and uncles. That’s easy enough to understand. It’s when you get to more distant connections that it becomes confusing.If you share the same grandparents, there is no difference in the generations, so you are first cousins. If you share the same great-grandparents, you are second cousins. If you share the same great-great-grandparents you are third cousins, and so on.However, if your grandparents are someone else’s great-grandparents, then you are first cousins once removed, because there is a generational gap between you. The thing to remember is that the “removed” is used when you and your relative are of different generations. For instance, you and your cousin’s child, or you and your father’s cousin are of different generations, so there is going to be a “removed” in a description of your relationship.The numerical value, “once removed” or “three times removed,” counts back how many generations you have to go to find the common ancestor between you and that other relative.For example, if your first cousin has children, those children are your first cousins once removed, because your grandparents are their great-grandparents (just one generation). If those children then have children, they are your first cousins twice removed, because your grandparents are their great-great-grandparents (which is two generations).Similarly, your mom’s cousin is your first cousin once removed, because his grandparents are your great-grandparents. There is a generational difference. However, your mom’s cousin’s CHILD is your second cousin with no “removed” added, because the two of you share the same great-grandparents. There is no generational difference between the two of you, so there is no “remove.”With regards to the difference between great-aunt, grand-aunt, etc. – this one is up to you! They're just different terms that mean the same thing. The siblings of your grandparents can be called either your great-aunts and great-uncles, or your grand-aunts and grand-uncles.The following chart may be helpful:The following DNA & Relationship Quick Reference Chart also helps identify the % of shared DNA between you and other relatives. Get your free pdf
2025-03-27Which I had taken pictures of when I visited her last spring, ancestry kit in hand. Our mutual cousin Ed had been there too and had given me his part of the tree. So I continued to enter their data, using censuses and those green leaves at ancestry to fill more in. MM’s grandad had 26 children so there are a lot of people in her tree.One fine September day I got an email from a Wold related 4th cousin asking if the new Wold test she was seeing was one of ours. So I opened MM’s results and found that another Wold cousin had tested at AncestryDNA, with the same name as my known 3rd cousin (MM’s 2nd once removed) . Sure enough, MM showed a 3rd cousin level match with him. I sent his son a note asking if that was really his Dad and eventually found out that yes it was.Time to check MM’s test for the common matches with our newly tested Wold cousin. Surprise! A is a shared match with him! Having both Wold and Goodsell matches, it would now seem that A is descended from Charley and Martha, most likely via one of MM’s aunts and thus is my relative too. Perhaps A is not MM’s second cousin after all, but a first cousin twice removed. This would be the case if A’s grandfather Gordon Johnson is MM’s first cousin. That relationship would share about the same amount of DNA as a second cousin. (Use the chart at ISOGG to determine other likely relationships from the amount of shared DNA – scan of the seven siblings of MM’s dad showed that one sister did marry a Johnson and had a son named Gordon! How did I not remember about A when I entered that
2025-04-17It Mean to be a Cousin “Once Removed”?Sometimes you and your cousin may share a common ancestor, but you each call this ancestor something different. For example, the common ancestor may be your great-grandparent, but your cousin’s great-great-grandparent. This is where the phrase “once removed” comes in handy.To be “once removed” from a cousin means you are separated by one generation. The number before “removed” will always represent the number of generations you are separated (“removed”) from the cousin. For example, if you are one generation away from your first cousin, then you are first cousins once removed. If you are two generations away from your second cousin, then you are second cousins twice removed.According to FamilySearch, you can use this chart to identify a cousin relationship without using a chart:For cousins that are in the same generation: determine the most recent common ancestor between the two people whose relationship you are trying to determine. Then use the “add 1” trick to find out what number cousin they are.For cousins that are not in the same generation: follow the steps above for the person who is more closely related to the common ancestor. Then determine the number of generations between the two potential cousins. Or conversely, determine how many generations further away from the common ancestor the second person is. Then add the “removed” phrase accordingly.ConclusionNow that you know how to calculate what kind of cousin your dad’s cousin is to you, you can explore your family tree more easily and confidently. You can also use this knowledge to connect with distant relatives and learn more about your ancestry and heritage. Remember, cousins are people who share a common ancestor with you that is at least two generations away. The number of generations determines what number cousin they are, and the difference in generations determines if they are “removed” or not. Happy researching!
2025-04-01(showing that they are grandchildren of the common progenitor); following their respective lines inward, they would come to rest in the space marked "1st cousin". In cases where one side descends the outside of the diamond further than the other side because of additional generations removed from the common progenitor, following the lines inward shows both the cousin rank (1st cousin, 2nd cousin) plus the number of times (generations) "removed".In the example provided at the right, generations one (child) through ten (8th great-grandchild) from the common progenitor are provided; however, the format of the chart can easily be expanded to accommodate any number of generations needed to resolve the question of relationship.See alsoCollateral descendantConsanguinityCousin marriageFamilyParallel and cross cousinsSiblingSecond-degree relativeReferences^ "Genetic And Quantitative Aspects Of Genealogy – Types Of Collateral Relationships". Genetic-genealogy.co.uk. Retrieved 28 October 2014.^ "What is a First Cousin, Twice Removed?". Genealogy.com. Retrieved Sep 26, 2015.^ "Sibling" would be a more accurate label for this box. Also, read "son|daughter" for "son", and "nephew|niece" for "nephew".External linksEuropean kinship systemGenealogy.com definition of various cousinsGenealogy.com: What makes a cousin?Genetic GenealogyFamily Relationship Chartv • d • eFamilyHistoryHouseholdNuclear familyExtended familyConjugal familyImmediate familyMatrifocal familyBlended familyDysfunctional familyPolyfidelitous familiesFirst-degree relativesParentFatherMotherChildSonDaughterSiblingBrotherSisterSecond-degree relativesGrandparentGrandchildAuntUncleNephewNieceThird-degree relatives1st cousinGreat grandparentGreat grandchildFourth-degree relatives2nd cousinGreat great grandparentGreat great grandchildFamily-in-lawSpouseHusbandWifeParents-in-lawSiblings-in-lawStepfamilyStepmotherStepfatherStepsiblingKinshipAdoptionAffinityConsanguinityDisownmentDivorceEstrangementFictive kinshipMarriageNurture kinshipLineageBilateral descentCommon ancestorFamily nameFamily treeGenealogyHeirloomHeredityInheritanceMatrilinealityPatrilinealityPedigree chartProgenitorRelationshipsAgape (parental love)Eros (marital love)Filial pietyPhilia (friendly love)Storge (familial love)
2025-04-19CNN — Janet Jackson has quite the family tree. In an interview with Scott Mills on BBC Sounds, Jackson was asked if it was true that she is related to another legendary singer, Stevie Wonder. “He’s our cousin,” Jackson said as Mills expressed shock. “Not a lot of people know that. He’s our cousin on my mother’s side.” But that wasn’t all. Jackson added, “So is Tracy Chapman. So is Samuel L. Jackson.” Mills was all of us as his mind was blown. He got Jackson to further confirm that Wonder, Chapman and Jackson are indeed all cousins. She even joked that Samuel L. Jackson, famed for his roles in films in “Pulp Fiction,” “Captain Marvel” and “Snakes on a Plane,” is not one of her brothers despite their shared last name. Janet Jackson is currently on a tour which celebrates her decades of hits. And she’s not the only Jackson family member who is riding the wave of success. Chapman, who is well known for being intensely private, has been enjoying a bit of a career revival, thanks to country artist Luke Combs covering her hit 1988 single “Fast Car.” That cover reaching No. 1 on the Country Airplay chart last year made Chapman the first Black woman to top the chart since the chart came into existence in 1990. She and Combs earned a standing ovation for their performance in February at the Grammys. CNN has reached out to representatives for Wonder, Chapman and Samuel L. Jackson for comment.
2025-03-30